Mazak MegaStir Friction Stir Welding (FSW)
Why Mazak MegaStir?
Mazak MegaStir offers machines, tools and consulting services for Friction Stir Welding (FSW) applications. We have an average of 20 years of experience specific to solid state joining, FSW, and Solid Deposition. There is no other company in the world which has more concentrated experience to draw from specific to these forms of Man Tech. Furthermore, our experience in tool and tool holder design is undisputed.
Overview of FSW technology
FSW effectively and consistently welds the latest generation of aluminum, steel and nickel-based alloys as well as a wide range of high-temperature and low-temperature metals. FSW welds without waste or toxic fumes, joins dissimilar alloys and solves geometric challenges.
Invented in 1991 by Wayne Thomas at TWI (The Welding Institute), Friction Stir Welding was initially regarded as an experimental process with few practical applications, if any. Over time, however, it soon became clear that FSW, which plasticizes material rather than melting it, not only rivaled but greatly improved upon traditional fusion welding techniques. The result is a technology that revolutionizes fabrication and offers a more efficient way to perform a wide range of industrial welding applications.
FSW process
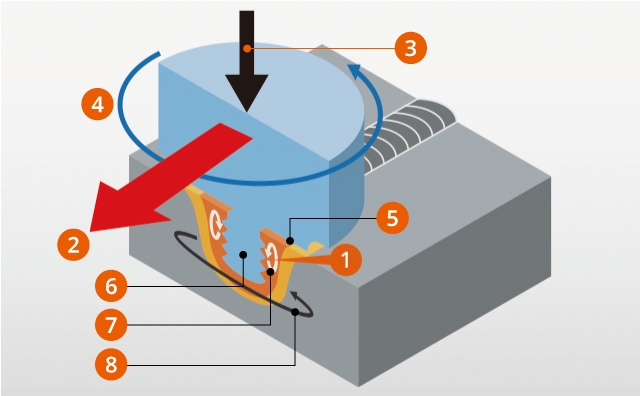
In FSW, a cylindrical shouldered tool with a profiled pin is rotated and plunged into the joint area between two pieces of sheet or plate material. The frictional heat between the wear-resistant welding tool and the workpieces causes the latter to soften without reaching the materials’ melting point, allowing the tool to traverse along the weld line without shielding gas or filler wire. The plasticized material, transferred to the trailing edge of the tool pin, is forged through contact with the tool shoulder and pin profile. On cooling, a solid phase bond is created between the workpieces.
- 1: Joint temperature below melting point
- 2: Junction direction
- 3: Tool thrust force
- 4: Direction of tool rotation
- 5: Shoulder
- 6: Probe
- 7: Axis direction plastic flow
- 8: Rotation direction plastic flow
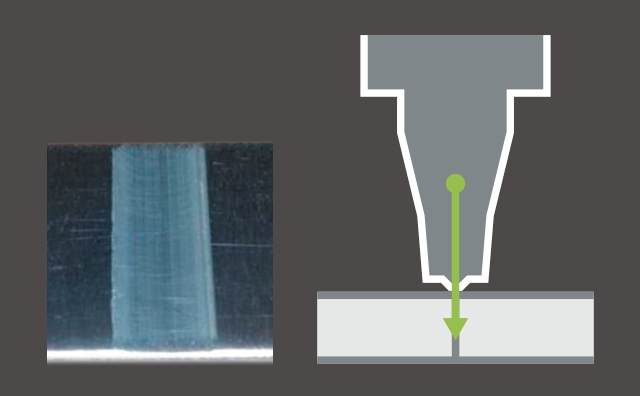
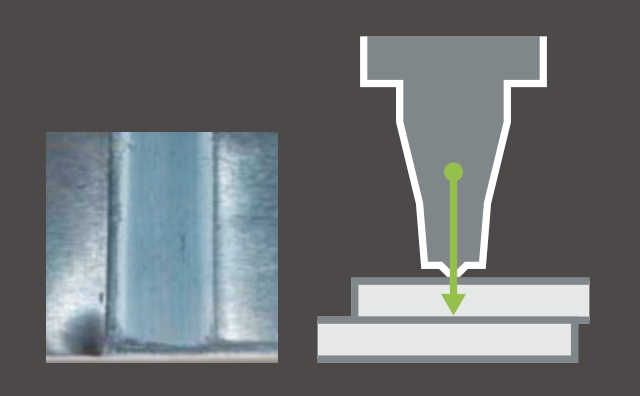
Production Benefits of FSW
Mazak’s unique FSW technology ensures stable joint quality.
Joint depth 0.12"
| Material | spindle speed |
| A6063 | 98 IPM |
| A5052 | 79 IPM |
| ADC12 | 59 IPM |
| C1020 | 12 IPM |
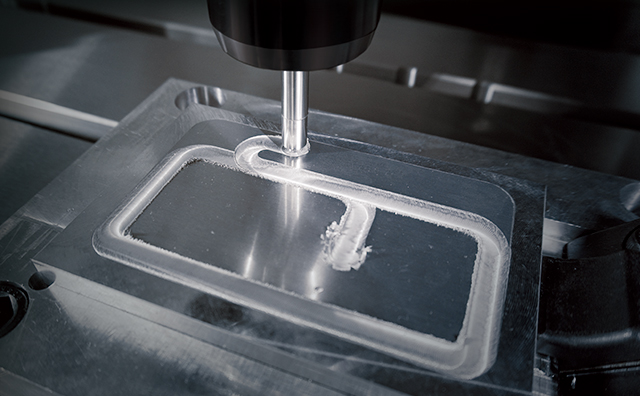
The Power of DONE IN ONE®
Only the combination of MegaStir FSW with that of Mazak HYBRID Multi-Tasking machine technology provides the benefits of DONE IN ONE part processing. With the ability to go from raw material to finished parts on one machine, manufacturers boost production throughput while also increasing part quality.
DONE IN ONE part processing also leads to Zero Steps manufacturing where operators take zero steps, there is zero scrap/rework and zero operational waste. Mazak HYBRID Multi-Tasking machines with FSW capability provide on-machine assembly that saves set-up time and eliminates errors associated with removing and transporting parts to assembly areas for joining operations.
With FSW, Mazak HYBRID Multi-Tasking machines gain additive manufacturing capability. FSW allows manufacturers to add stock material to or join additional components and assemblies to existing parts then quickly finish machine them to size.
Friction Bit Joining (FBJ)
In tandem with FSW technology, Mazak MegaStir patented a process known as Friction Bit Joining (FBJ). The process, like FSW, gives manufacturers the ability to join two dissimilar metals without comprising their individual inherent properties or strengths. Where other joining processes would fail to provide significant bond strength when joining two different materials, FBJ generates a powerful metallurgical bond between the process’ bit, which is a consumable, and the first and second metals, generating a solid state joint that is flush on both sides.
Benefits of FBJ
- Achieve holding strength greater than other traditional self-piercing processes as well as spot welding.
- Pierce through and join high-strength dissimilar metals, such as 7000 series aluminum and advanced high-strength steels such as DP 1200, that self-piercing rivets are unable to penetrate.
- Replace traditional through-hole riveting that sacrifices strength at the joint and requires additional material preparation to create through holes prior to actual riveting.






![FSW-460V [High-speed FSW] Friction Stir Welding Example of battery case welding [JIMTOF2022 exhibition machine] FSW-460V](/adobe/dynamicmedia/deliver/dm-aid--3dd69e9a-d552-4fee-b697-a1b70938eaa3/lgollfyo-ei.jpg?preferwebp=true&width=1920&quality=100)